© Franck Barbier





La préhistoire : Structured Analysis and Design Technique -SADT-, Yourdon's structured method, Information Engineering -IE-, Axial, Merise, GRAI…
Années 80 : apparition et prise de leadership des « langages orientés objet » (C++…) imposant les « méthodes orientées objet » : Object Modeling Technique -OMT-, Object-Oriented Analysis and Design -OOAD-, Objectory (a.k.a. Object Oriented Software Engineering -OOSE-) et beaucoup d'autres (ROOM, OOSA, OOA/OOD, Syntropy, Specification and Description Language -SDL-…)
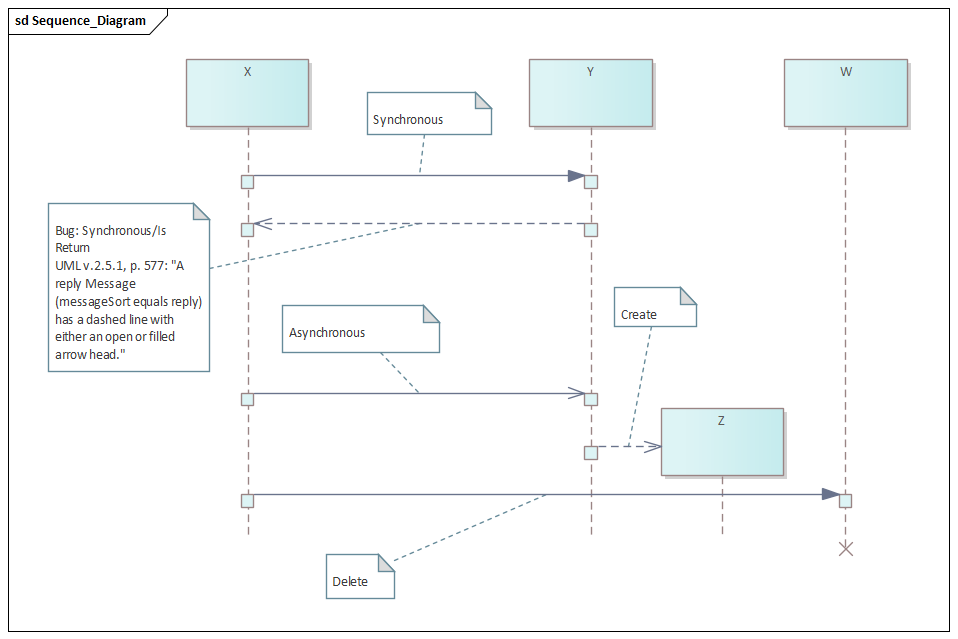
Le passé récent : Unified Method 0.8 (Booch + Rumbaugh), UML 0.9 and 1.0 (+ Jacobson), UML 1.1 (OMG, 1997), UML 2.0 (2003) -Structure, Behavior, Object Constraint Language -OCL- 2.0, XML Model Interchange -XMI-, UML 2.1.1 (Feb. 2007) et finalement UML 2.5.1 (Dec. 2017 -PDF-)
Le présent : BPMN, SysML (ingénierie « système »), ArchiMate (“Enterprise Architecture Modeling”) et toujours UML
L'exigence : modélisation avec agilité

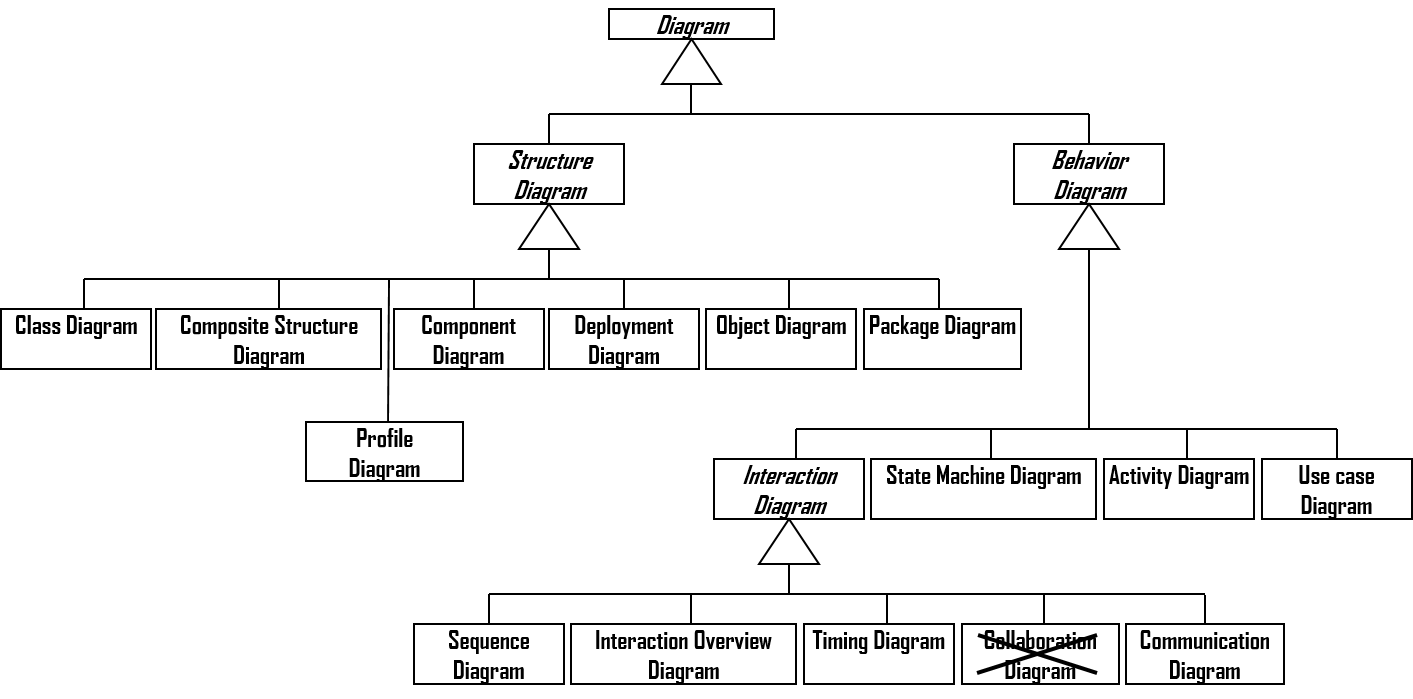
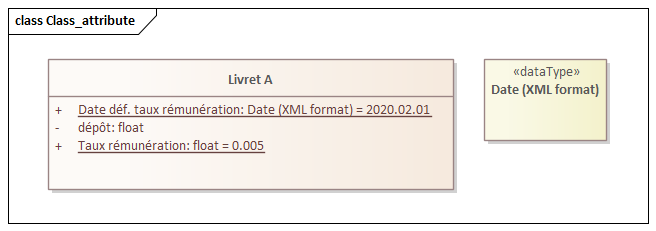
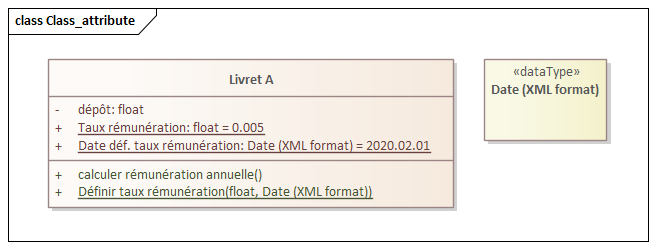
Class, Attribute, Operation,
State, Actor, Collaboration, Activity)




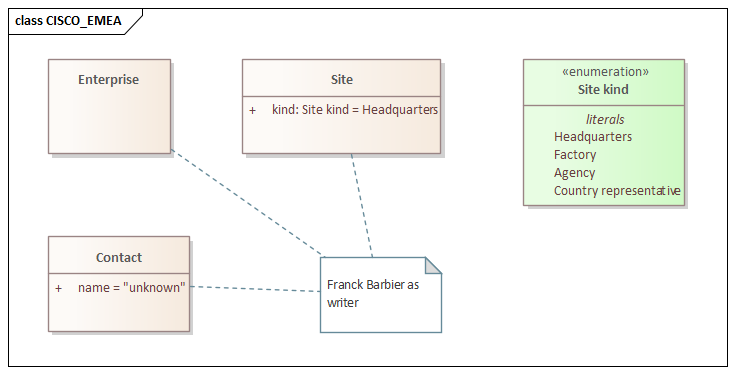
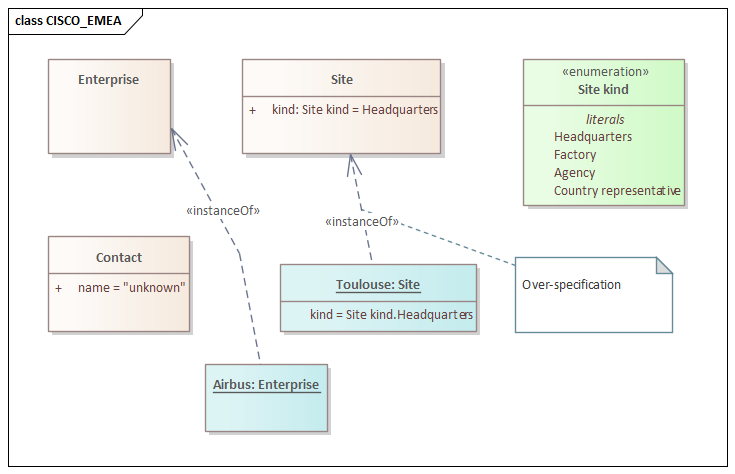
*Annotation on element with built-in stereotypes («class», «interface», «instanceOf», «enumeration»…)
or possibility of defining new ones






*{unique}
and {unordered} are default constraints
on association ends; {nonunique}
and {ordered} are counterparts when default constraints do not apply

0..1
1 (≡ 1..1)
0..* (≡ *)
1..*
1..6
2,4,6,8,10..* (custom)
even (custom)
prime (custom)


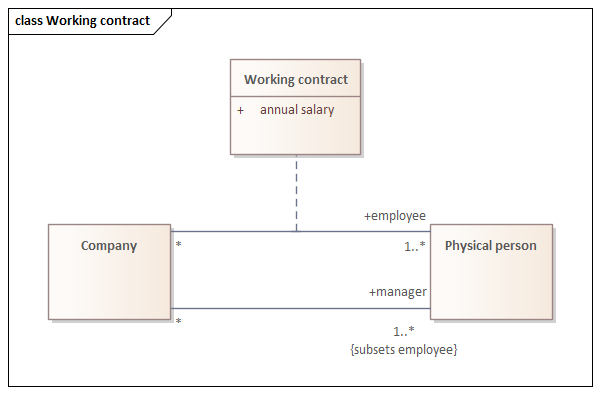
{subsets} constraint on UML Association*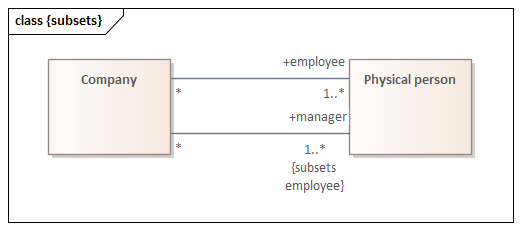
*OCL
context Company inv: employee->includesAll(manager)
{xor} constraint on UML Association*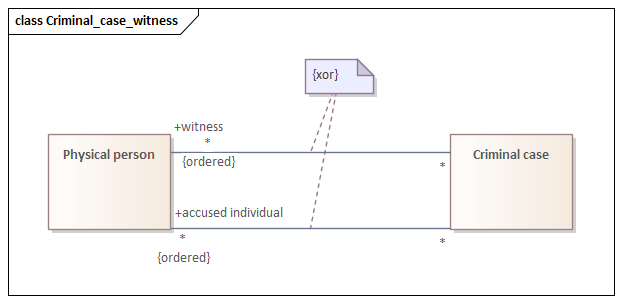
*OCL
context Criminal case inv: witness->intersection(accused individual)->isEmpty()

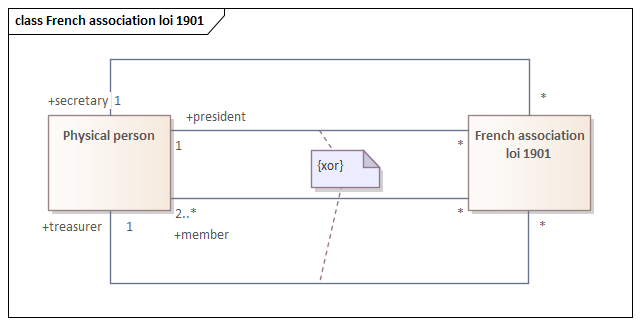

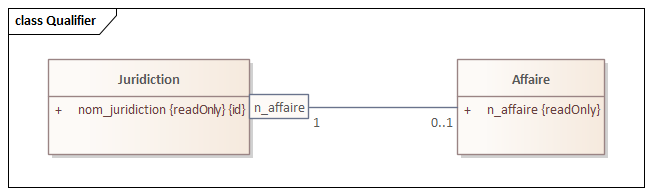
*OCL
context Juridiction inv: -- this constraint is redundant with the qualifier
affaire[n_affaire]->size() <= 1context Affaire inv: id.
self->isUnique(juridiction.nom_juridiction.concat(n_affaire))




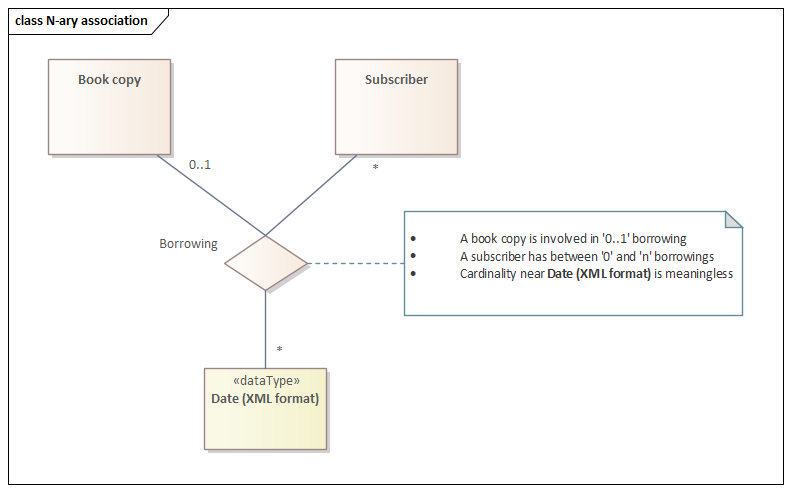

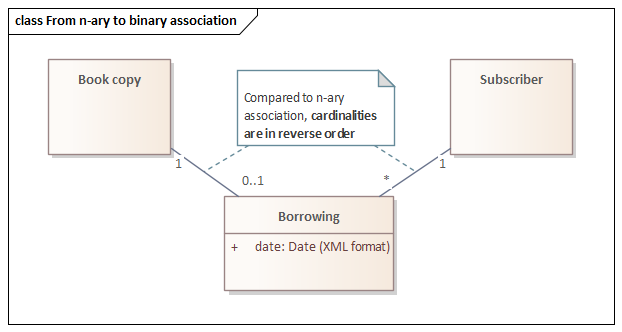

*OCL
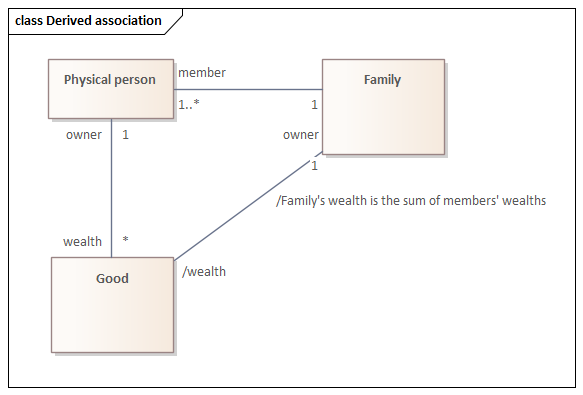
context Family inv: self.wealth = self.member.wealth
Straight line class,y = a * x + b

Straight line
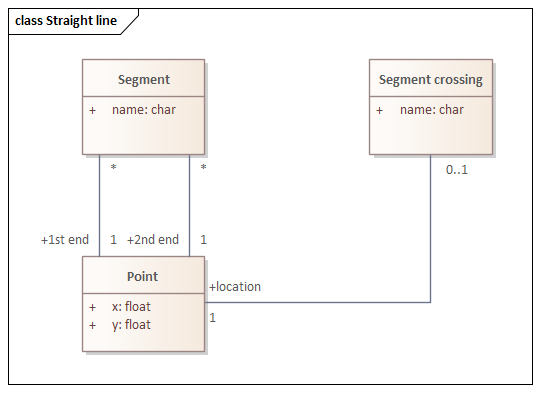

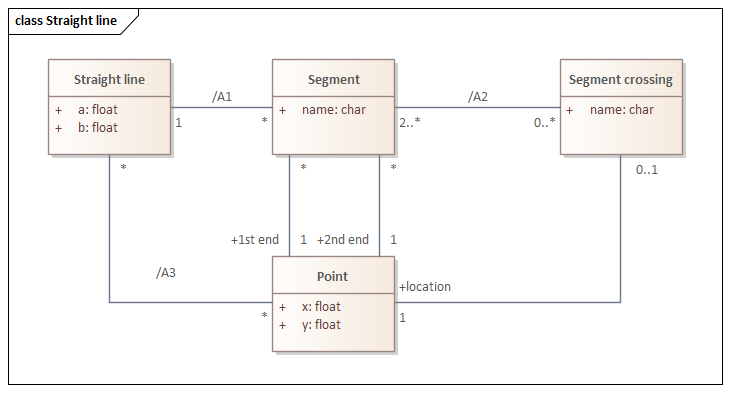

context Segment inv:
1st end.x = 2nd end.x implies 1st end.y <> 2nd end.ycontext Segment inv: A1
straight line = Straight line.allInstances()->select(sl | sl.a = (2nd end.y – 1st end.y) /
(2nd end.x – 1st end.x) and sl.b = 2nd end.y - sl.a * 2nd end.x)context Segment crossing inv: A2
segment = Segment.allInstances()->select(s | location.y =
s.straight line.a * location.x + s.straight line.b)context Point inv: A3
straight line = Straight line.allInstances()->select(sl | y = sl.a * x + sl.b)context Segment crossing inv:
segment.straight line.point->includes(location)
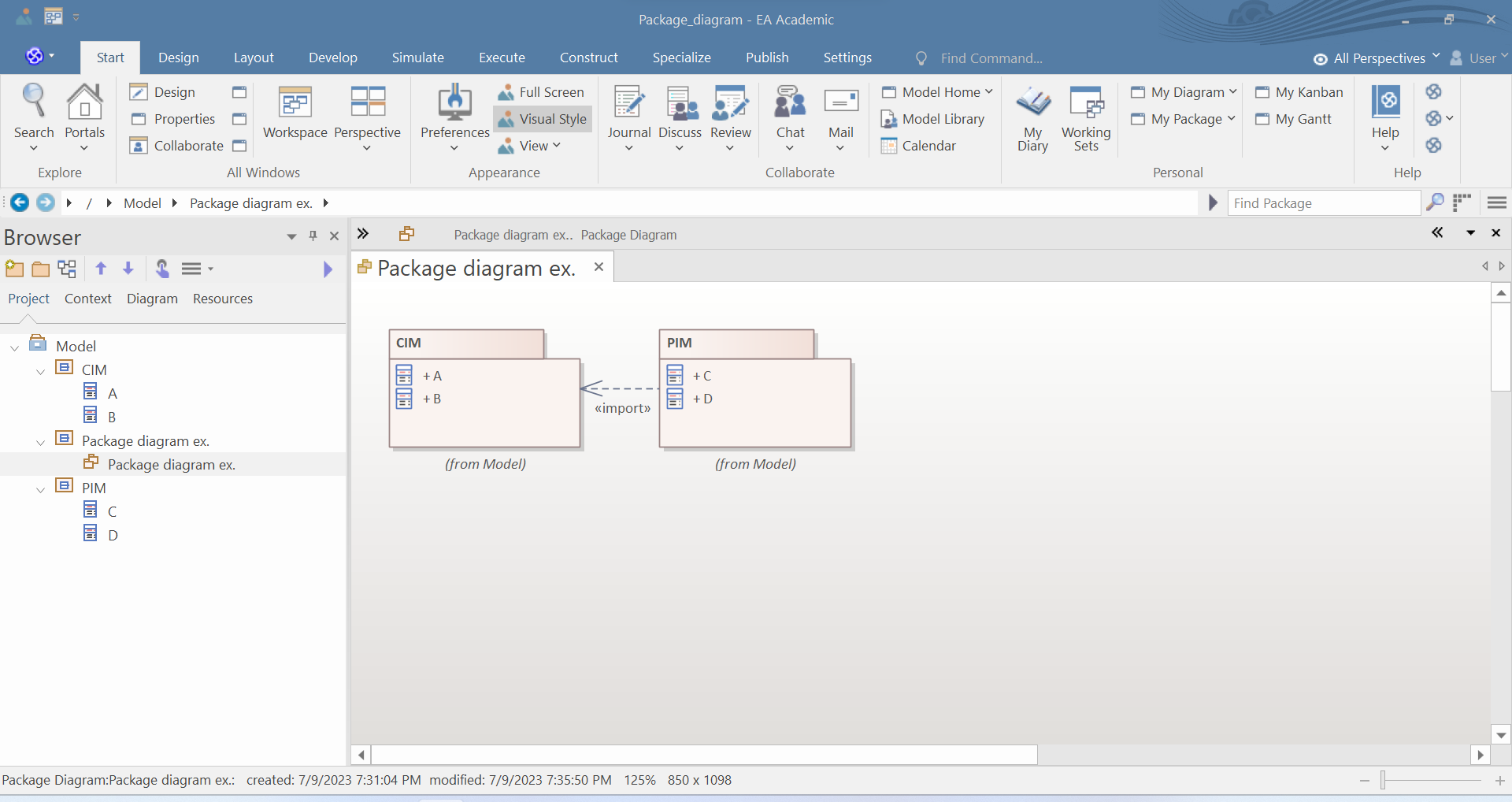


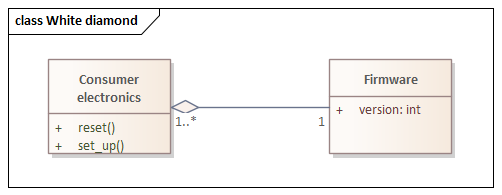

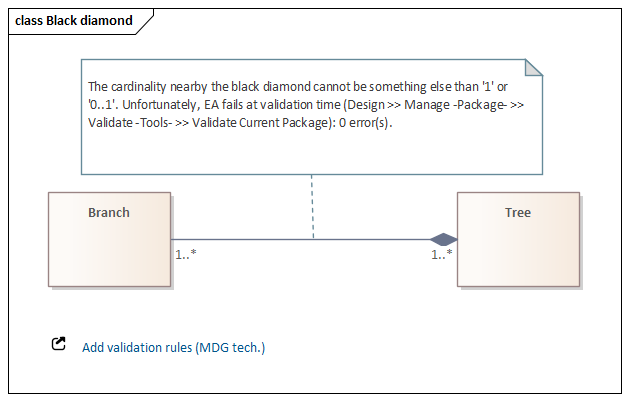


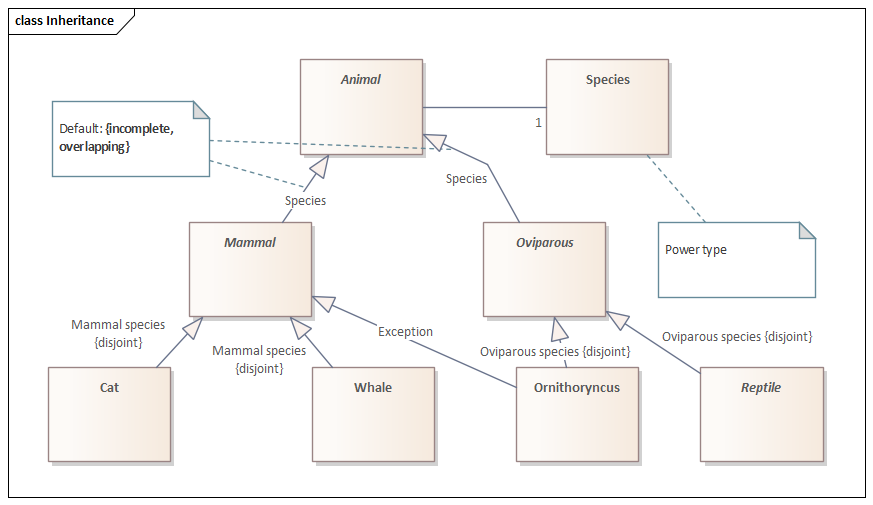
Alternatives to default: {complete, disjoint}, {disjoint},
and {complete}

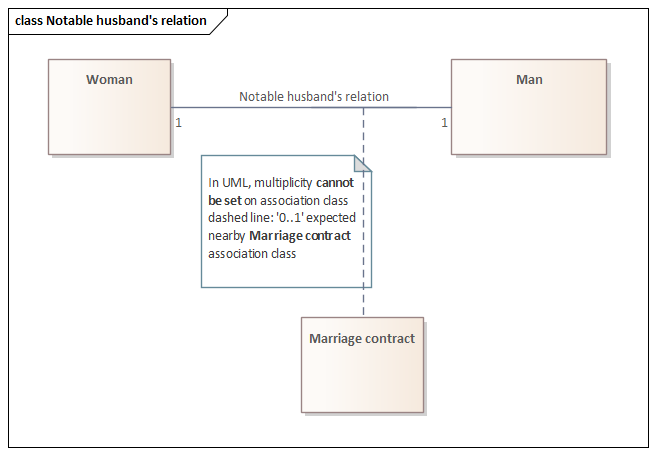
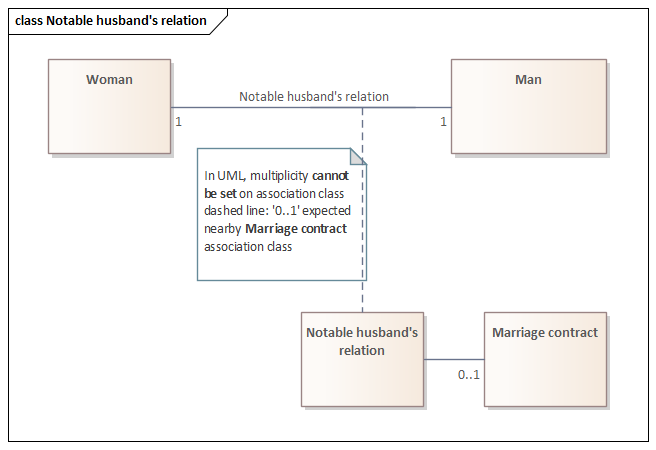
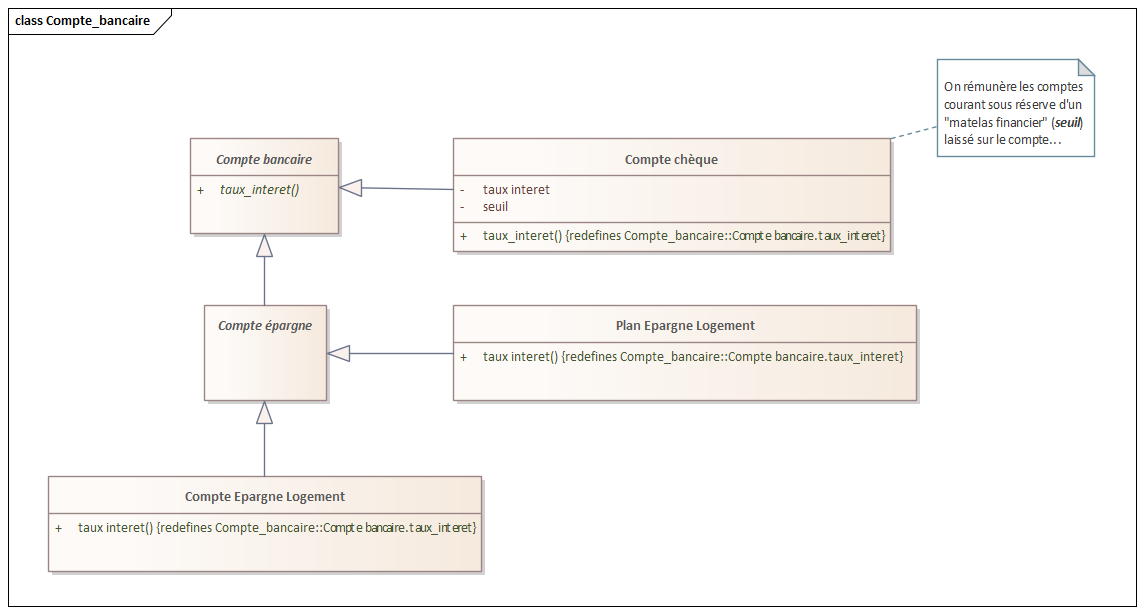
{redefines} constraint on UML Association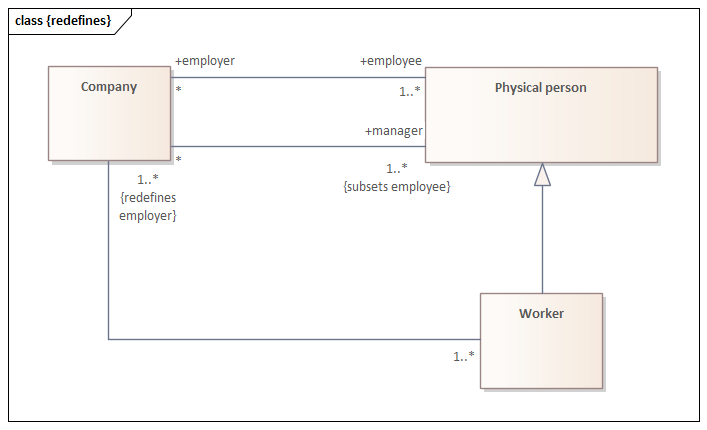



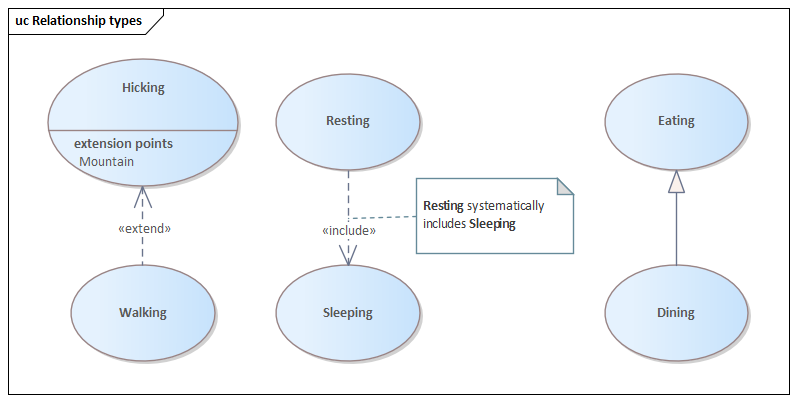

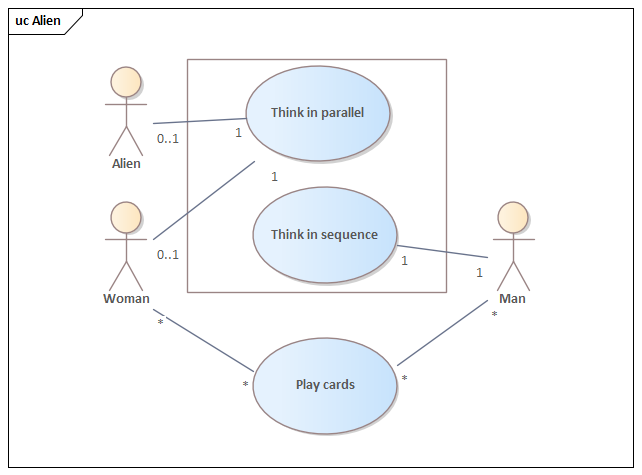

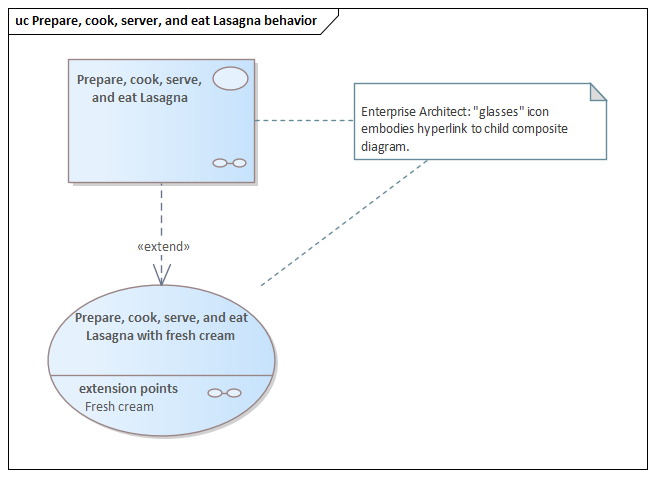

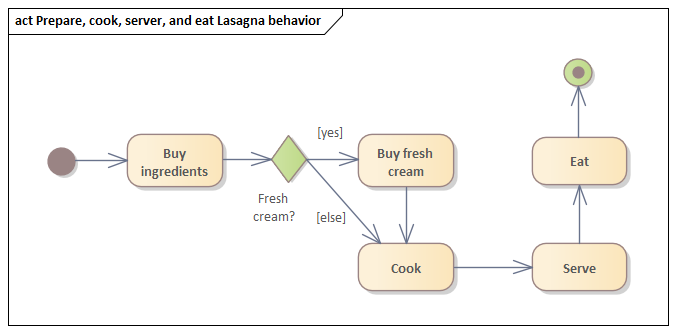





*«ownedBehavior» meta-association


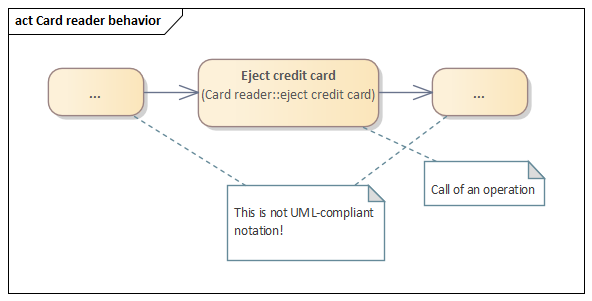
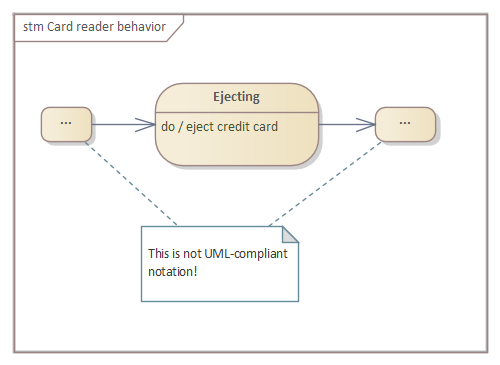
*«ownedBehavior» meta-association

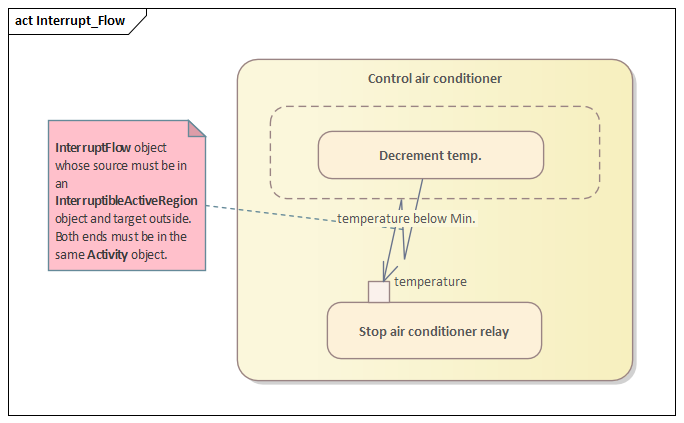

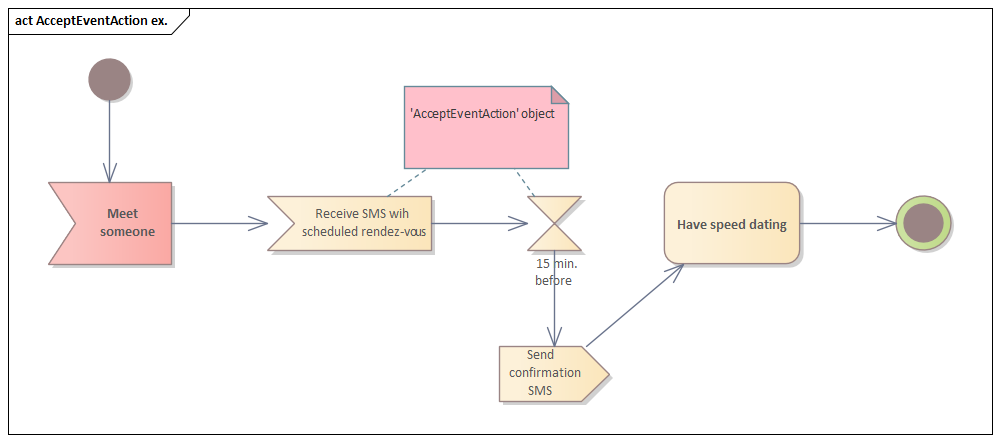

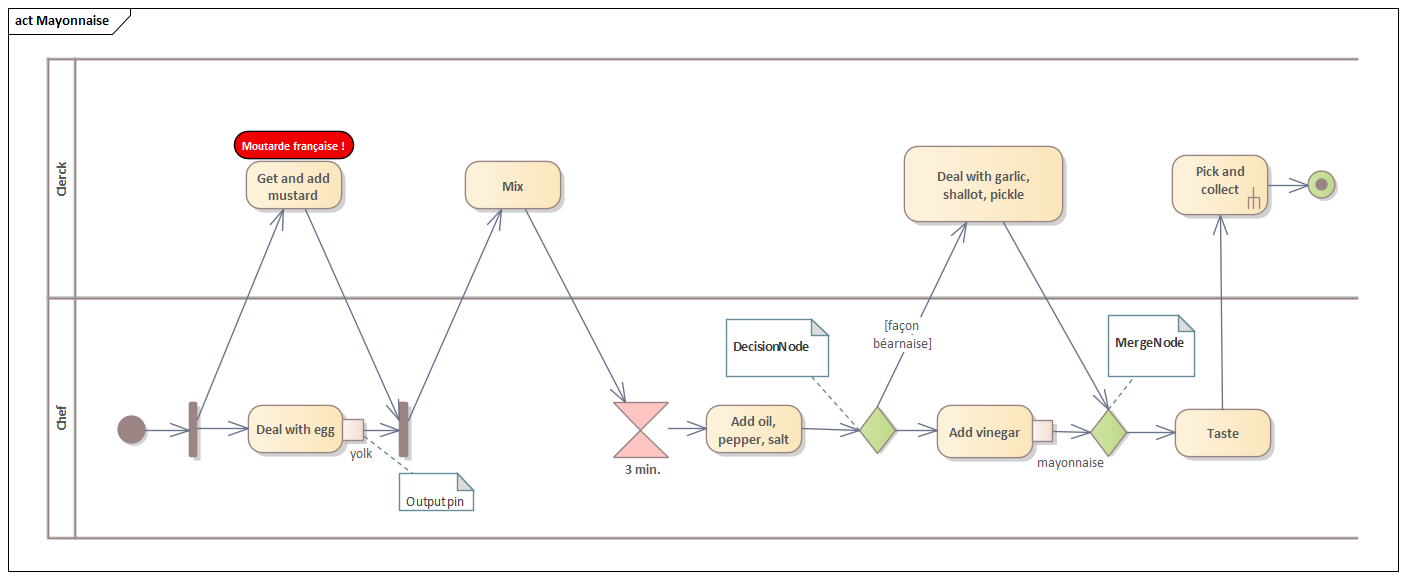



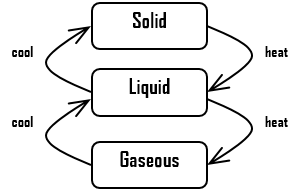


entry, do, exit, internal transition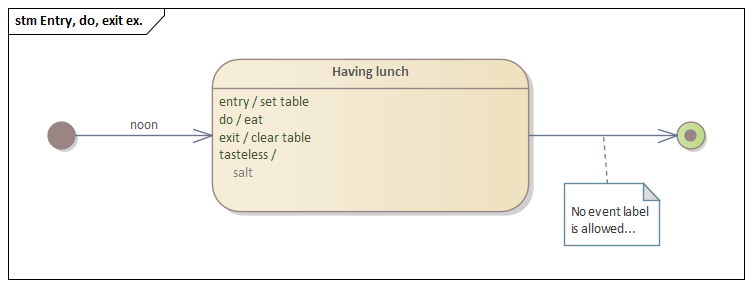

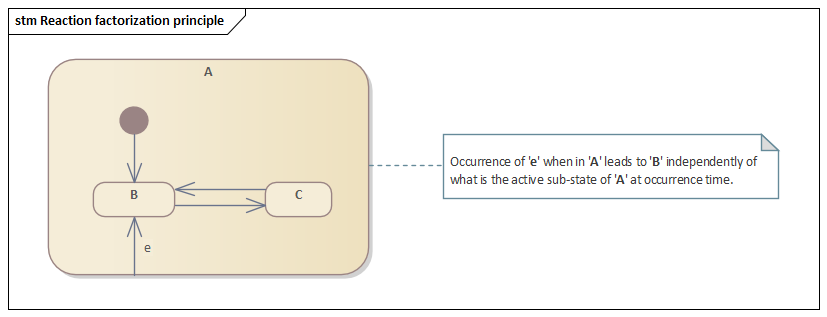

in operator)



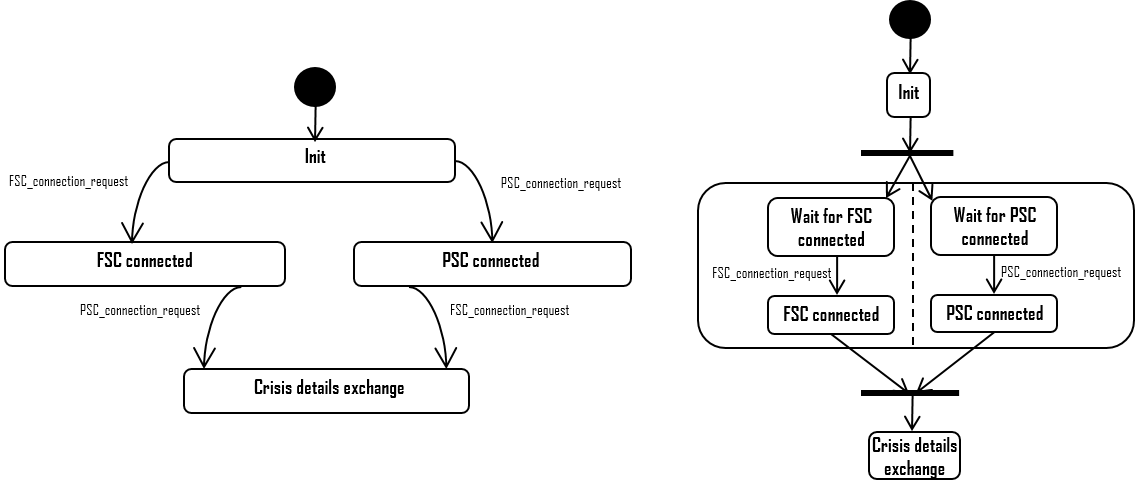

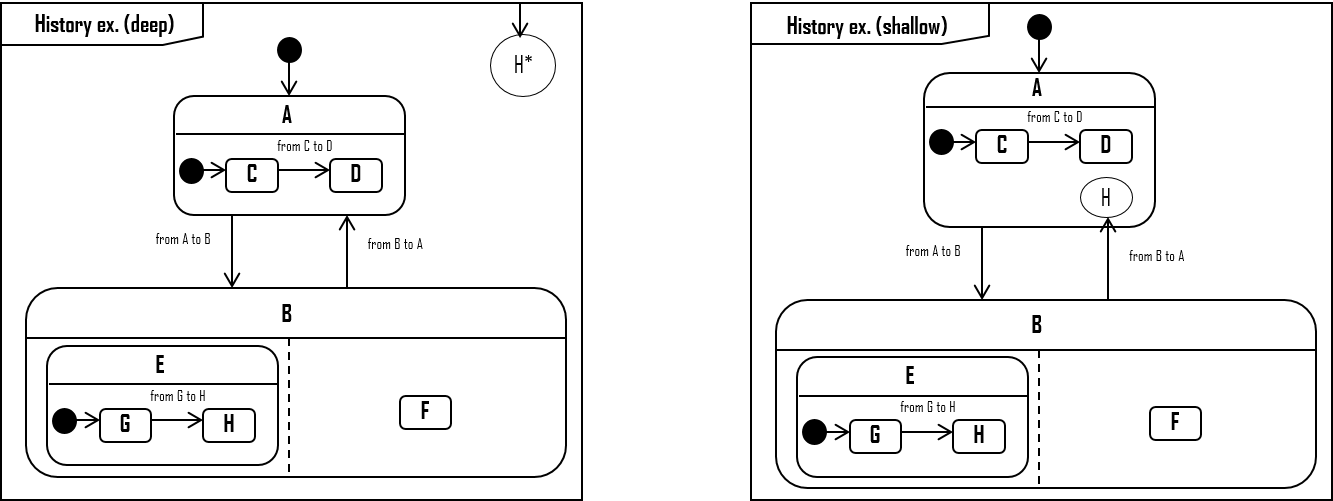
*See also ☛ for execution


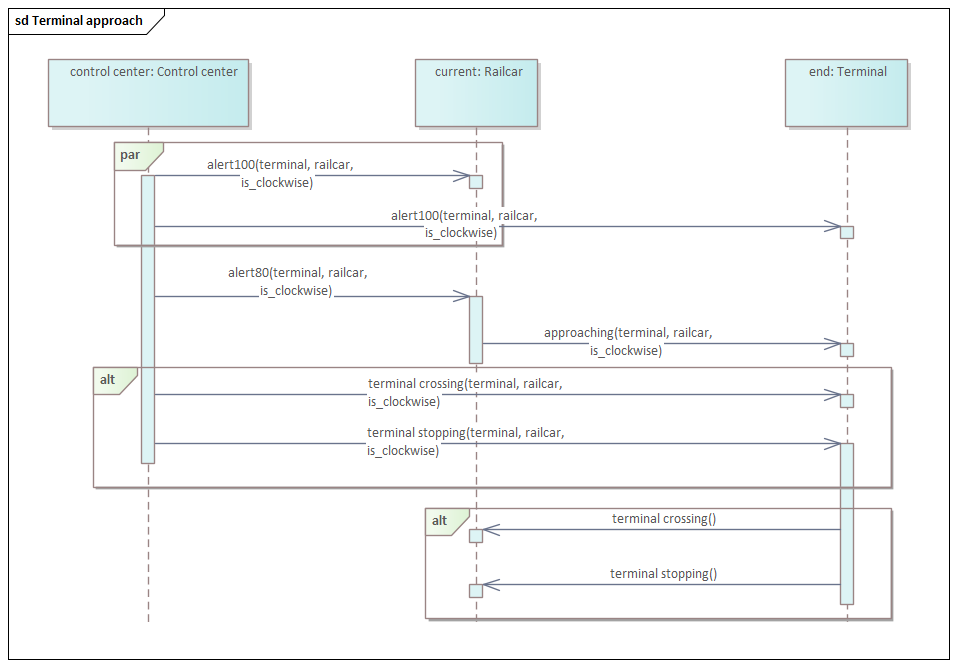
*alt, opt, par, seq, break, critical, neg & strict