
What is current shell?
# '-bash' ⤳ '.bash_profile' or '-zsh' ⤳ '.zshrc' echo $0Status of last execution?
echo $?
Status of last execution?
Write-Output $? // 'True' ('0') or 'False' ('1' or '2') # Alternative: $LASTEXITCODE
WebAssembly ☛ is a technology to write code that runs within the Web, both on the client side (browser) and the server side (e.g., Node.js) or more generally the cloud. On the client side, browser compatibility may be checked from ☛
On the server side, WebAssembly is the highway to serverless computing based on the idea of serverless function within the cloud
Beyond browsers and Node.js as WebAssembly runtime supports, non-Web WebAssembly runtime supports proliferate ☛
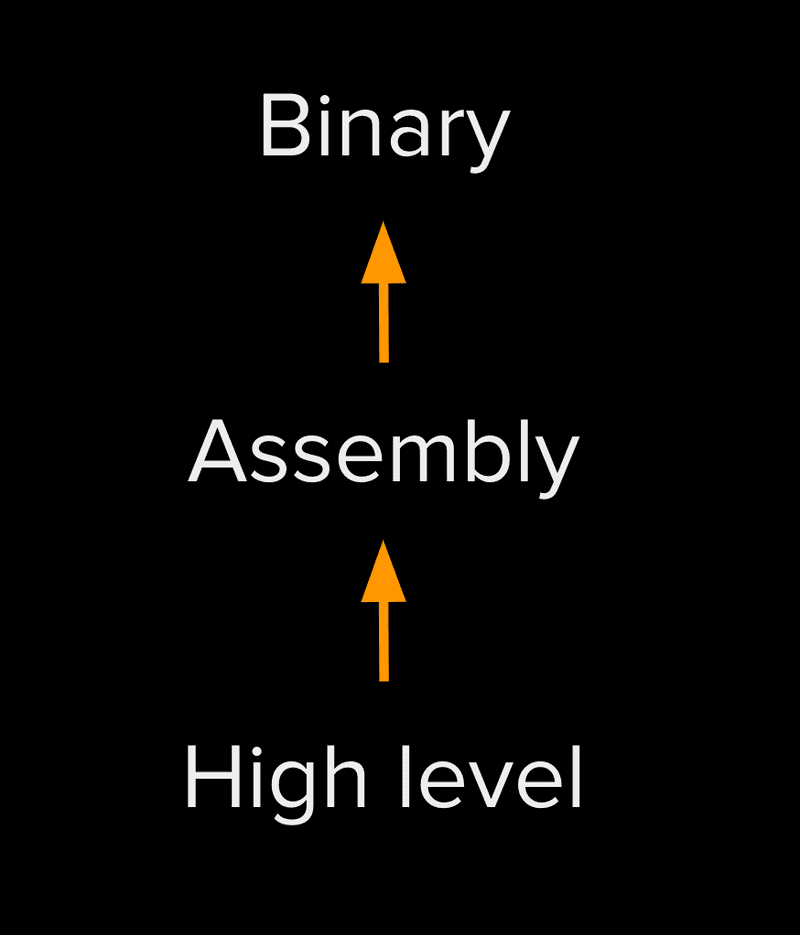
As named, WebAssembly is a neutral (assembly) language whose ultimate end is to produce native code by means of a C compiler. In the meantime, source code may be written in any (high-level) programming language, say, AssemblyScript
Many tutorials on WebAssembly exist throughout the Web
Credit: J. YoungThe foundation of WebAssembly, notably the fact that WebAssembly is nothing else than a virtual machine (a.k.a. conceptual machine) is in deep developed ☛
Binaryen is the compiler (optimizer as well) to compile to WebAssembly. It is used by most “high-level” programming languages like AssemblyScript to produce
.watand.wasmcodeBinaryen does not require specific installation because it is installed by third-party software in general
WebAssembly text format (
.watsuffix) ☛ is the most straightforward way of creating a WebAssembly functionWebAssembly text format (
.watsuffix) is a typed language using builtin types ☛Example What_year_.wat

(module (func (export "what_year_") (result i32) ;; No parameter... i32.const 2025 return ) )The translation from WebAssembly text format (
.watsuffix) to WebAssembly assembler (.wasmsuffix) relies on a perfect one-to-one mapping between the text format and the assembler. Conversion from.wasmto.watis then seamless as wellThe “perfect” one-to-one mapping relies on a stack machine whose functioning is detailed ☛ (see “How the code works: a stack machine” section)
Example What_year_.wasm

0000000: 0061 736d ; WASM_BINARY_MAGIC 0000004: 0100 0000 ; WASM_BINARY_VERSION ; section "Type" (1) 0000008: 01 ; section code 0000009: 00 ; section size (guess) 000000a: 01 ; num types ; func type 0 000000b: 60 ; func 000000c: 00 ; num params 000000d: 01 ; num results 000000e: 7f ; i32 0000009: 05 ; FIXUP section size ; section "Function" (3) 000000f: 03 ; section code 0000010: 00 ; section size (guess) 0000011: 01 ; num functions 0000012: 00 ; function 0 signature index 0000010: 02 ; FIXUP section size ; section "Export" (7) 0000013: 07 ; section code 0000014: 00 ; section size (guess) 0000015: 01 ; num exports 0000016: 0a ; string length 0000017: 7768 6174 5f79 6561 725f what_year_ ; export name 0000021: 00 ; export kind 0000022: 00 ; export func index 0000014: 0e ; FIXUP section size ; section "Code" (10) 0000023: 0a ; section code 0000024: 00 ; section size (guess) 0000025: 01 ; num functions ; function body 0 0000026: 00 ; func body size (guess) 0000027: 00 ; local decl count 0000028: 41 ; i32.const 0000029: e90f ; i32 literal 000002b: 0f ; return 000002c: 0b ; end 0000026: 06 ; FIXUP func body size 0000024: 08 ; FIXUP section size ; section "name" 000002d: 00 ; section code 000002e: 00 ; section size (guess) 000002f: 04 ; string length 0000030: 6e61 6d65 name ; custom section name 0000034: 02 ; local name type 0000035: 00 ; subsection size (guess) 0000036: 01 ; num functions 0000037: 00 ; function index 0000038: 00 ; num locals 0000035: 03 ; FIXUP subsection size 000002e: 0a ; FIXUP section sizeOnline Web converters
Execution next relies on a WebAssembly runtime support like Wasmtime ☛
Wasmtime installation ☛
Example What_year_.wasm
What_year_.wat

wasmtime run --invoke what_year_ What_year_.wasm# Translation precedes execution: wasmtime run --invoke what_year_ What_year_.watWebAssembly text format: the “stack machine”
Example
;; '(;' <- is equivalent to '/*' while ';)' <- is equivalent to '*/' (; (func (param i32) (param f32) (local f64) local.get 0 local.get 1 local.get 2 …) ;) ;; '$' allows naming instead using numeric indexes: 0, 1, 2... ;; (func (param $first_parameter i32) (param $second_parameter f32) (local $local_variable f64) ;; local.get $first_parameter ;; local.get $second_parameter ;; local.get $local_variable ;; …)Other formats
.wast☛ is a superset of.wat. Use of named parameters above, e.g.,local.get $first_parameteris rather part of.wastwhilelocal.get 0is rather part of.wat.cwasmis a kind of.wasmin the sense that it refers toAhead-Of-Time-AOT- compilation (opposite toJust-In-Time-JIT- compilation).wit☛ is a textual format to express Wasm Interface Type -WIT- components: “worlds” embody components with “interfaces” and without implementations.wacwhich stands for WebAssembly Compositions -WAC- is a superset of the WIT textual format
AssemblyScript getting started ☛
Once installed, AssemblyScript compiler version may be displayed
asc -v # Download, cache et let access to AssemblyScript compiler (first execution time) before use: # Alternative: 'npx asc -v'Rule(s)
- AssemblyScript has, compared to TypeScript, its own types ☛ like, for instance,
i32oru32(unsigned 32-bit integer). In constrast, TypeScript core types, namelyanyandunknown, are not part of AssemblyScript- Although AssemblyScript is inspired by TypeScript, there are significant differences ☛
Example
Barcode_checksum.tsBarcode.WebAssembly.zip
// Entry file to generate WebAssembly module, i.e., 'Barcode_checksum.wat'/'Barcode_checksum.wasm' export function Barcode_checksum(barcode: i64): i32 { // You can only export functions that call methods on an instance passed to them: const checksum = (new EAN(barcode.toString())).correct; // Host function from AssemblyScript standard library... Cannot work with 'Wasmtime' or 'WasmEdge': // console.info(checksum.toString()); return checksum; // '0', '-1' or '-2' } // https://www.assemblyscript.org/concepts.html#special-imports // Compilation: 'asc assembly/Barcode.ts --target release --use abort=assembly/Barcode_checksum/Abort' function Abort(message: usize, fileName: usize, line: u32, column: u32): void { // Overriding 'abort' from 'env' (e.g., Node.js: 'process.exit(1);') } // AssemblyScript enumerated types can only be backed by 'i32': enum Result { Correct /* = "Correct" */, Incorrect = -1 /* = "Incorrect" */, Invalid_format = -2 /* = "Invalid format" */ } // 'Only variables, functions and enums become WebAssembly module exports.': /* export default */ class EAN { // Regular expressions are not native in AssemblyScript: // static readonly Format: RegExp = new RegExp("^(?!000)(\\d{13}$)"); static readonly Thirteen: i32 = 13; private readonly _data: Array<i32> = new Array; private _correct: Result = Result.Invalid_format; // Default value... get correct(): Result { return this._correct; } constructor(barcode: string) { if (barcode.length === EAN.Thirteen) { // barcode.split("").every(function (s: string) { // 'barcode' is divided into individual numbers... // // JavaScript 'parseInt' returns 'f64' format that requires explicit casting in AssemblyScript: // const element: i32 = parseInt(s) as i32; // Conversion for computations... // if (isNaN(element)) return false; // 'every' stops with 'this._correct === Result.Invalid_format'... // // Closures not yet implemented (https://blog.bitsrc.io/typescript-to-webassembly-the-what-the-how-and-the-why-3916a2561d37): // this._data.push(element); // Bug... // return true; // 'every' goes on... // }); // Substitute for closure: const elements = barcode.split(""); for (let i = 0; i < elements.length; i++) { const element: i32 = parseInt(elements[i]) as i32; if (isNaN(element)) break; this._data.push(element); } this._correct = this._checksum() === this._data[EAN.Thirteen - 1] ? Result.Correct : Result.Incorrect; } } private _checksum(): i32 { // Méthode : https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/EAN_13#Calcul_de_la_cl%C3%A9_de_contr%C3%B4le_EAN_13 // '471-9-5120-0288-x' with 'x' as checksum (i.e., 'x === 9') // '7', '9', '1', '0', '2', '8' const remainder = (this._data.filter((element: i32, index: i32) => index % 2 !== 0) .reduce((result, element) => result + 3 * element, 0) + // '4', '1', '5', '2', '0', '8' this._data.filter((element: i32, index: i32) => index % 2 === 0 && index !== EAN.Thirteen - 1) .reduce((result, element) => result + element, 0)) % 10; return remainder === 0 ? 0 : 10 - remainder; } }Rule(s)
- The AssemblyScript compiler generates two files from
Barcode_checksum.ts
Barcode_checksum.wat(WebAssembly text format based on symbolic expressions found in programming languages like List Processing -LisP-)Barcode_checksum.wasm(assembler)Execution
# Checksum is correct, i.e., '0' wasmtime --invoke Barcode_checksum ./build/Barcode_checksum.wasm 4719512002889 # Checksum is incorrect, i.e., '-1' wasmtime --invoke Barcode_checksum ./build/Barcode_checksum.wasm 4719512002888Host function: the case of JavaScript
Rule(s)
- Simply speaking, exported (provided) functions in WebAssembly modules (e.g.,
Barcode_checksum) compute output data that aim at being pushed as input data in other functions. The need for Input/Output support then relies on WebAssembly itself (WebAssembly System Interface -WASI-) or homemade support- To that extent, AssemblyScript provides a standard library including JavaScript “commonalities”, say,
console,process… with local functions, say,infoforconsole,exitforprocess… These are (facilitation) host functions- By construction, host functions are imported in WebAssembly modules (
Barcode_checksum.watandBarcode_checksum.wasm). If no host bindings are provided then no executions are possible within WebAssembly runtime supportsExample
export function Barcode_checksum(barcode: i64): i32 { // You can only export functions that call methods on an instance passed to them: const checksum = (new EAN(barcode.toString())).correct; // Host function from AssemblyScript standard library... Cannot work with 'Wasmtime' or 'WasmEdge': console.info(checksum.toString()); return checksum; // '0', '-1' or '-2' }
Barcode.watfile(import "env" "console.info" (func $~lib/bindings/dom/console.info (param i32)))Exercise ☛
Creation of a WebAssembly module may rely on varied programming languages ☛. Ultimately,
.watand.wasmfiles provide computational matter in a programming language-agnostic matterTinyGo installation on macOS
brew install go brew tap tinygo-org/tools # Binaryen also installed: brew install tinygoGo ☛ and TinyGo installation on Windows
# Scoop install. first... Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope CurrentUser; Invoke-RestMethod -Uri https://get.scoop.sh | Invoke-Expression# WASI access at compilation time requires 'binaryen': choco install go; scoop install tinygo; scoop install binaryenOnce installed, Go and TinyGo compiler version may be displayed
go version# Forthcoming 'build' fails on Windows if 'Temp' directory does not exist... tinygo version; tinygo --help; mkdir C:\Temptinygo build --helpTinyGo support for WebAssembly
Example
Barcode_checksum.goBarcode.WebAssembly.zip
package main import ( "fmt" "strconv" "strings" ) func main() {} type Result int const ( Correct Result = iota Incorrect Invalid_format ) // The following comment is *MANDATORY to get the 'Barcode_checksum' function "exported": //export Barcode_checksum func Barcode_checksum(barcode int64) Result { _barcode := strconv.FormatInt(barcode, 10) // values := []byte(_barcode) // Get ASCII values... elements := strings.Split(_barcode, "") if len(elements) == 13 { _data := [13]int{} for index, character := range elements { element, error := strconv.Atoi(character) if error != nil { return Invalid_format } _data[index] = element } if _Checksum(_data) == _data[len(_data)-1] { fmt.Println("Barcode: " + _barcode + " is correct...") // WASI support generated by '-target=wasi' at build time... return Correct } return Incorrect } return Invalid_format } func _Checksum(_data [13]int) int { remainder := 0 for index, datum := range _data { if index%2 != 0 { remainder += 3 * datum } } for index, datum := range _data { if index%2 == 0 && index != len(_data)-1 { remainder += datum } } if remainder%10 == 0 { return 0 } return 10 - remainder%10 }Build using WASI ☛
- WASI ver. 0.1.0:
-target=wasior-target=wasip1- WASI ver. 0.2.x:
-target=wasip2tinygo build -o ./TinyGo/Barcode_checksum.wasm -target=wasi ./TinyGo/Barcode_checksum.goExecution
# Checksum is correct, i.e., '0' wasmtime --invoke Barcode_checksum ./TinyGo/Barcode_checksum.wasm 4719512002889 # Checksum is incorrect, i.e., '1' wasmtime --invoke Barcode_checksum ./TinyGo/Barcode_checksum.wasm 4719512002888Exercise ☛
Using wazero ☛ (macOS)
~/bin/wazero version# Problem to call a specific named function, i.e., 'Barcode_checksum': ~/bin/wazero run ./TinyGo/Barcode_checksum.wasm 4719512002889
Rule(s)
- Common JavaScript programs may run WebAssembly modules by using the WebAssembly JavaScript API ☛
Client side (browser)
AssemblyScript compiler automatically generates JavaScript stuff (e.g.,
Barcode_checksum.js) to run a WebAssembly module on the client side (browser) using the WebAssembly JavaScript API ☛Example Barcode.WebAssembly.zip

<!-- Use of default JavaScript file is generated by AssemblyScript --> <script type="module"> import {Barcode_checksum} from "./build/Barcode_checksum.js"; window.document.body.innerText = Barcode_checksum(4719512002889n); </script>Instead, one may customize the way the WebAssembly JavaScript API ☛ is used
Example
Using_Barcode_checksum.wasm_client_side.jsBarcode.WebAssembly.zip
window.fetch("./build/Barcode_checksum.wasm").then(bytes => bytes.arrayBuffer()).then(async buffer => { window.console.assert(buffer instanceof ArrayBuffer); const module = await WebAssembly.compile(buffer); window.console.assert(module instanceof WebAssembly.Module); // Etc. });Example
Using_Barcode_checksum.wasm_client_side.jsBarcode.WebAssembly.zip
/** Compilation is such that 'abort' is bypassed: * 'asc assembly/Barcode_checksum.ts --target release --use abort=assembly/Barcode_checksum/Abort' * As a result, AssemblyScript compiler no longer imports 'abort'... (https://www.assemblyscript.org/concepts.html#special-imports), * but 'console.info(checksum.toString());' requires binding: */ const import_ = {env: {"console.info": data => console.info(`'console.info': ${data}`)}}; // 'import_' is *REQUIRED* in 'WebAssembly.instantiateStreaming' // only if the instantiated module actually imports something (https://stackoverflow.com/questions/48039547/webassembly-typeerror-webassembly-instantiation-imports-argument-must-be-pres) WebAssembly.instantiateStreaming(window.fetch("./build/Barcode_checksum.wasm"), import_).then(web_assembly => { window.console.assert(web_assembly.module instanceof window.WebAssembly.Module); window.console.assert(web_assembly.instance instanceof window.WebAssembly.Instance); // Memory provided by WebAssembly module (https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/WebAssembly/JavaScript_interface/Memory): const memory = web_assembly.instance.exports.memory; window.console.assert(memory instanceof WebAssembly.Memory && memory.buffer instanceof ArrayBuffer); // Alter 'memory' ('ArrayBuffer' objects cannot be directly handled): // const data = new DataView(memory.buffer); const imports = WebAssembly.Module.imports(web_assembly.module); // Array of declared imports... for (const import_ of imports) window.console.log(JSON.stringify(import_)); // 'imports[0]': '{"module":"env","name":"console.info","kind":"function"}' window.console.assert("Barcode_checksum" in web_assembly.instance.exports); window.document.body.innerText = web_assembly.instance.exports.Barcode_checksum(4719512002889n); // Display '0' meaning "OK"... }, error => { window.console.error(error); // window.alert(error); });Server side (e.g., Node.js ☛)
AssemblyScript compiler automatically generates JavaScript stuff (e.g.,
Barcode_checksum.js) to run a WebAssembly module on the server side using the WebAssembly JavaScript API ☛Example
Using_Barcode_checksum.wasm_server_side.mjsBarcode.WebAssembly.zip
import path from 'path'; import {fileURLToPath} from 'url'; import {Barcode_checksum} from "../build/Barcode_checksum.js"; // JavaScript file is generated by AssemblyScript! // Display the fact that executable file extension is '.mjs' so that Node.js uses ES module technology // Note: 'ReferenceError: __dirname is not defined in ES module scope' const __filename = fileURLToPath(import.meta.url); const __dirname = path.dirname(__filename); console.info("\t" + __filename + " WITHIN " + __dirname); console.assert(typeof Barcode_checksum === 'function'); console.info("\t" + 'Barcode_checksum(4719512002889n): ' + Barcode_checksum(4719512002889n)); // '0' means "OK"...
WebAssembly great deal is memory! There are several good tutorials on this: ☛ and ☛
Imported memory from host, e.g., JavaScript on the client side (browser)
Example
Memory.watMemory.wat.zip(module (; '0' is the number of pages in the default memory (1 page = 65536 bytes) ;) (; Name of memory within JavaScript: 'memory_from_JavaScript.memory_within_module' ;) (import "memory_from_JavaScript" "memory_within_module" (memory 0)) (data (i32.const 0) "Franck Barbier") ;; String is stored in the 'memory_within_module' object from position '0'... (func (export "get_length") (result i32) i32.const 14 ;; Data length return ) )Allocate memory to WebAssembly module
Example
Memory.jsMemory.wat.zip// JavaScript creates a WebAssembly-based memory object: const memory_from_JavaScript = new WebAssembly.Memory({initial: 1}); // 1 page - 65536 bytes // Translation using WABT: 'wat2wasm Memory.wat -o Memory.wasm' WebAssembly.compileStreaming(window.fetch("./Memory.wasm")) // "importObject" is *REQUIRED* when the instantiated module actually imports something: .then((module) => WebAssembly.instantiate(module, { memory_from_JavaScript: {memory_within_module: memory_from_JavaScript} })) .then((executable) => { window.console.assert(executable instanceof WebAssembly.Instance); const length = executable.exports.get_length(); // '(func (export "get_length")…' const bytes = new Uint8Array(memory_from_JavaScript.buffer, 0, length); window.alert(new TextDecoder('UTF8').decode(bytes)); // "Franck Barbier" });General approach
.wat(import "a" "f" (func ...)) (import "a" "g" (func ...)) (import "b" "m" (memory 0)).watconst import_ = { a: {f: function (...) {...}, g: function (...) {...}}, b: {m: new WebAssembly.Memory(...)} }; WebAssembly.instantiate(module, import_).then(executable => { window.console.assert(executable instanceof WebAssembly.Instance); // Etc.Imported function from host, e.g., JavaScript on the client side (browser)
Example
Memory_size.watMemory.wat.zip(module (; Client-side (browser) JavaScript function is imported: ;) (import "window" "alert" (func $window_alert (param i32))) (memory 10) ;; 655360 bytes (func (export "Memory_size") memory.size ;; Put the "memory size" on the stack... call $window_alert ;; Call through local name, i.e., '$window_alert' ) )Example
Memory_size.jsMemory.wat.zip// Browser only! WebAssembly.instantiateStreaming(window.fetch("./Memory_size.wasm"), {window: {alert: window.alert}}) .then(web_assembly => { window.console.assert("Memory_size" in web_assembly.instance.exports); web_assembly.instance.exports.Memory_size(); // 10 pages... });Exported memory
Rule(s)
- WebAssembly non-numerical types, (i.e., types different from integers like
i64, reals likef64…), strings typically, must be handled through memory pages (1 page: 65536 bytes). To that extent,WebAssembly.Memorytype allows the handling of WebAssembly memory within the WebAssembly JavaScript API ☛- WebAssembly modules may own memory pages and export them. The WebAssembly JavaScript API ☛ may then access them through, if exported,
instance.exports.my_memory_nameunder the following condition:window.console.assert(instance instanceof WebAssembly.Instance)Example
Exported_memory.watMemory.wat.zip(; Multiple memories do not work! ;) ;; https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/WebAssembly/Understanding_the_text_format#multiple_memories (module (import "env" "log" (func $display_character (param i32))) ;; Only one memory block is allowed: (memory $my_page 1) ;; [0-65535] ;; "RuntimeError: WebAssembly.instantiate(): data segment 0 is out of bounds" -> ;; (memory $my_page 0) ;; No space is allowed! (export "My_page" (memory $my_page)) (data (i32.const 0) "'$my_page' is ") ;; Add "'$my_page' is " to default (0-index) memory... (data (memory 0) (i32.const 14) "writte") (func $main i32.const 20 ;; Position... i32.const 110 ;; 'n' character... i32.store8 ;; 'n' character is stored... ;; (i32.store8 (i32.const 20) (i32.const 110)) ;; 'n' character is stored at position '20'... (i32.load8_s (i32.const 19)) ;; Get character at 'position '19' for display... call $display_character ;; 101 => 'e' ) (start $main) )Example
Exported_memory.jsMemory.wat.zipWebAssembly.instantiateStreaming(fetch("./Exported_memory.wasm"), {env: {log: console.log}}) // Bind actual host function to "virtual" imported function within module... .then(({instance}) => { // '{instance}' means "get 'instance' field"... const my_page = instance.exports.My_page; // Exported memory... const bytes = new Uint8Array(my_page.buffer, 0, 21); // < 65536 console.info(new TextDecoder('UTF8').decode(bytes)); // '$my_page' is written });Exercise
Create
Exercise.watfile, which records ($Indexglobal variable) the first available position in memory. This has to occur with regard to an exportedPopulatefunction that stores bytes from$Indexand next increments$Index
Exercise.wat(module (memory 1) ;; [0-65535] (global $Index (mut i32) (i32.const 0)) ;; Index of first available position... (func $Get (export "Get") (result i32) global.get $Index ) (func $Set (param i32) local.get 0 ;; Get parameter... global.set $Index ) ;; 'Populate' exported function... )(module (memory 1) ;; [0-65535] (global $Index (mut i32) (i32.const 0)) ;; Index of first available position... (func $Get (export "Get") (result i32) global.get $Index ) (func $Set (param i32) local.get 0 ;; Get parameter... global.set $Index ) (func (export "Populate") (param $data i64) i32.const 8 ;; 8 bytes have to be stored... call $Get ;; Index of first available position <= 65535 i32.add i32.const 65535 i32.gt_u ;; 'i32.add' is greater than '65535' (if (then unreachable) (else call $Get ;; Index of first available position <= 65535 local.get $data ;; Data (8 bytes) to be stored... i64.store i32.const 8 ;; 8 bytes have just been stored... call $Get i32.add call $Set ;; Increment... ) ) ) )Test: call multiple times
PopulatewithinExercise.jsfile
Exercise.jsWebAssembly.instantiateStreaming(fetch("./Exercise.wasm")) .then(web_assembly => { window.console.assert("Get" in web_assembly.instance.exports); window.console.assert("Populate" in web_assembly.instance.exports); console.info("$Index: " + web_assembly.instance.exports.Get()); // '0' web_assembly.instance.exports.Populate(2025n); // '2025' as BigInt, i.e., using 'n' window.alert("$Index: " + web_assembly.instance.exports.Get()); // '8' });Variables ☛
Global variables may be imported to allow basic memory sharing between modules or with JavaScript (client side -browser- and server side -e.g., Node.js-). For the sake of security, only immutable variables may be exported…
Example
;; Module for sharing data only... (module (global $PI f32 (f32.const 3.14159)) ;; Immutable by default... (export "PI" (global $PI)) (func $nop) ;; It's mandatory since no exported function exists... )
Rule(s)
- The lack of resource access and consumption facilities in WebAssembly modules leads to WebAssembly System Interface -WASI-: original paper ☛ (March 2019)
- WASI is promoted by the Bytecode Alliance ☛, which includes Amazon, Google, Microsoft, Intel…
- The key issue behind WebAssembly is the fact that, by nature, a module has no access (and therefore consumption possibility) of “host” resources. For example, access to the file system in Node.js (as “host”) is based on the
fsobject. A WebAssembly module cannot deal with files in general throughfsin Node.js- Official WASI specification ☛
AssemblyScript
as-wasi☛ is the WASI support in AssemblyScript. However, it seems to be no longer maintained ☛as-wasi☛ exposes resources and possible usages (e.g.,WASI.Console.logbelow) in a standardized way (i.e., WASI) avoiding the use of convenient AssemblyScript host functions specific to JavaScript (e.g.,console.log)- WASI aims at creating total neutrality within AssemblyScript code. WebAssembly modules written in AssemblyScript or competitor programming languages like Rust, then have agnostic mechanisms in
.watand.wasmfiles in the way, the host execution context is interacted withExample
Barcode_checksum_WASI.tsBarcode.WebAssembly.zip
import * as WASI from "as-wasi/assembly"; import {Barcode_checksum} from "./Barcode_checksum"; // Access and consume command line arguments from host: const barcode: string = WASI.CommandLine.all[0].includes("node") ? WASI.CommandLine.all[2] : WASI.CommandLine.all[1]; // Wasmtime WASI.Console.log("\t\t(WebAssembly module hosted) Barcode: " + barcode); let checksum: i32 = Barcode_checksum(I64.parseInt(barcode)); WASI.Console.log("\t\t(WebAssembly module hosted) Checksum: " + checksum.toString()); checksum = WASI.CommandLine.all[0].includes("node") ? checksum : -checksum; // Wasmtime requires [0..126) interval... WASI.Process.exit(checksum); // Node.js: '0', '-1' or '-2' versus Wasmtime: '0', '1' or '2'Note:
wasi_abort, which is equivalent to POSIXSIGTERM, is not available within"as-wasi": "^0.6.0". Version"as-wasi": "^0.5.1"is required.asc assembly/Barcode_checksum_WASI.ts --exportStart _start --outFile ./build/Barcode_checksum_WASI.wasm --textFile ./build/Barcode_checksum_WASI.wat --target release --use abort=wasi_abortNode.js execution involves the
--experimental-wasi-unstable-preview1option. Execution relies onBarcode_checksum_WASI.jsJavaScript file generated by AssemblyScript: it does not work…node --experimental-wasi-unstable-preview1 ./build/Barcode_checksum_WASI.js 4719512002889Instead, execution based on Wasmtime works fine…
wasmtime --invoke _start ./build/Barcode_checksum_WASI.wasm 4719512002889AssemblyScript
exportRuntimecompiler option (default istrue) provides C-like primitives (e.g.,__new) to deal with pointers within JavaScript. As expected, host memory is the first resource a WebAssembly module aims at dealing withasconfig.jsonfile"options": { "bindings": "esm", "exportRuntime": true, // "exportStart": "_start" // Command line instead... }, …WASI, the case of Node.js ☛
Rule(s)
*Node.js WASI API imposes that the “start” function must be explicitly named
- Node.js provides a builtin API for WASI* ☛
- Principle: Node.js “pushes” its execution context to WASI, namely
env,process… The executed WebAssembly module having Node.js as host transparently accesses and consumes resources from this execution context using a Portable Operating System Interface X -POSIX-, which is a compliant entry point namedwasi_snapshot_preview1☛_startExample
Using_Barcode_checksum.wasm_server_side_WASI.mjsas Node.js host program Barcode.WebAssembly.zip
import {readFile} from 'node:fs/promises'; import {env} from 'node:process'; import {WASI} from 'node:wasi'; console.info("\t(Node.js host) Version: " + process.version); console.info("\t(Node.js host) Current directory: " + process.cwd()); console.info("\t(Node.js host) Barcode: " + process.argv[2]); const module = await WebAssembly.compile(await readFile(new URL('../build/Barcode_checksum_WASI.wasm', import.meta.url))); // https://nodejs.org/api/wasi.html#new-wasioptions const wasi = new WASI({ args: process.argv, // Node.js command line arguments are passed to the WebAssembly module env, // Caution here: 'process.env' is *ACTUALLY* passed to 'wasi'... preopens: { '/sandbox': process.cwd() // Access to resource(s) in current directory... }, returnOnExit: true, // 'wasi.start()' returns the exit code to Node.js... version: 'preview1' // Mandatory! }); // Imported object is required, i.e., the API itself to access resource(s): const instance = await WebAssembly.instantiate(module, wasi.getImportObject()); // Node.js WASI API imposes that the start method must be explicitly named '_start': const checksum = wasi.start(instance); // '0', '-1' or '-2' console.info("\t(Node.js host) Checksum: " + checksum); process.exit(checksum); // Node.js returns the exit code to Operating System -OS- (Windows: 'Write-Output $?' -> 'True' or 'False')...Execution
node --experimental-wasi-unstable-preview1 ./js/Using_Barcode_checksum.wasm_server_side_WASI.mjs 4719512002889
macOS
curl https://wasmtime.dev/install.sh -sSf | bashWindows PowerShell ☛
Version and help
wasmtime -V; wasmtime --helpRule(s)
- Wasmtime is a very direct way of operating WASI and therefore WebAssembly. As standalone runtime support, Wasmtime is a non-Web (i.e., outside browsers and Node.js) WebAssembly middleware
- Wasmtime may be operated via a Command Line Interface -CLI- or as a library. For example, Go programs may embed Wasmtime in order to run WebAssembly modules ☛. Wasmtime distinguishes “command” modules for execution within the CLI from “reactor” modules, which rather aims at being commissioned (i.e., distributed and brought into services) ☛
Execution ☛ encompasses native code (e.g., Windows) production from compilation, and chained sandboxed execution
Example
Global_variable.watMemory.wat.zip
(module ;; Global_variable.wat (global $YEAR (mut i32) (i32.const 2024)) ;; Mutable global var. (func $Happy_new_year (param $value i32) (result i32) local.get $value ;; Push '$value' arg. on the stack global.set $YEAR ;; Set '$YEAR' to current value on the stack global.get $YEAR ;; Push '$YEAR' on the stack for return... ;; return ;; May be omitted... ) (func (export "_start") ;; '_start' is the default expected name avoiding '--invoke' option using Wasmtime... (result i32) i32.const 2025 ;; Push '2025' as argument for 'Happy_new_year' call $Happy_new_year ;; return ;; May be omitted... ) )Translation
.wat⤳.wasmand nextAhead-Of-Time-AOT- compilation (.cwasmformat) followed by executionwasmtime compile Global_variable.wat; wasmtime run --allow-precompiled Global_variable.cwasmExecution (
runmay be omitted): translation.wat⤳.wasmand nextJust-In-Time-JIT- compilation followed by executionwasmtime run Global_variable.watExample
Multiple_memories.watMemory.wat.zip
(module ;; Multiple_memories.wat ;; Check 'multi memory' from https://webassembly.github.io/wabt/demo/wat2wasm/ (memory $my_own_memory_0 10) ;; 10 pages... (memory $my_own_memory_1 20) (data (memory 0) (i32.const 0) "Franck") ;; String is stored in the default (0-index) memory from position '0'... (data (memory 1) (i32.const 0) "Bar") ;; String is stored in the (1-index) memory from position '0'... (data (memory $my_own_memory_1) (i32.const 3) "bier") ;; String is stored in the (1-index) memory from position '3'... (func (export "_start") (result i32) call $_ranges i32.sub ;; Size of string is returned ) (func $_ranges (result i32 i32) i32.const 5 ;; Final storing position i32.const 0 ;; Initial storing position ) (func (export "SIZE") (result i32) (memory.size)) ;; '10' ;; Does not work, but translation to .wasm succeeds: ;; (func (export "SIZE_") (result i32) (memory.size (memory $my_own_memory_1))) (func (export "GET") (param i32) (result i32) ;; '0' -> 70 ('F'), '1' -> 114 ('r')... (i32.load8_s (local.get 0)) ) ;; Does not work, but translation to .wasm succeeds: ;; (func (export "GET_") (param i32) (result i32) ;; '0' -> 65 ('B')... ;; (i32.load8_s (memory $my_own_memory_1) (local.get 0)) ;; ) )# Display -> 5 wasmtime Multiple_memories.wat# Display -> 10 wasmtime --invoke SIZE Multiple_memories.wat# Display -> 70 -> 'F' wasmtime --invoke GET Multiple_memories.wat 0WASI, the case of Wasmtime ☛
asc assembly/Barcode_checksum_WASI.ts --exportStart _start --outFile ./build/Barcode_checksum_WASI.wasm --textFile ./build/Barcode_checksum_WASI.wat --target release --use abort=wasi_abortwasmtime --invoke _start ./build/Barcode_checksum_WASI.wasm 4719512002889
Note: instead of Wasmtime, WasmEdge does not directly deal with the
.watformatInstallation ☛
macOS including WebAssembly System Interface -WASI-
curl -sSf https://raw.githubusercontent.com/WasmEdge/WasmEdge/master/utils/install.sh | bash -s -- --plugins wasi_nn-ggmlOr…
curl -sSf https://raw.githubusercontent.com/WasmEdge/WasmEdge/master/utils/install_v2.sh | bashOr…
brew install wasmedgeWindows PowerShell including WebAssembly System Interface -WASI-
winget upgrade wasmedgeOnce installed, version and help may be displayed
wasmedge -v; wasmedge -hRunning WebAssembly code
Example What_year_.wasm

# JIT compilation wasmedge What_year_.wasm what_year_Compiling WebAssembly code ☛
Example What_year_.wasm

# AOT compilation wasmedge compile --enable-time-measuring What_year_.wasm What_year_.cwasmmacOS
# "In the reactor mode, wasmedge runs a specified function exported by the WebAssembly program." time wasmedge --reactor What_year_.wasm what_year_ time wasmedge --reactor What_year_.cwasm what_year_Windows PowerShell
Measure-Command {wasmedge --reactor What_year_.wasm what_year_} Measure-Command {wasmedge --reactor What_year_.cwasm what_year_}Running third-party code, the case JavaScript ☛
Code is developed through C++, Go, JavaScript, Python or Rust ☛. As forJavaScript ☛, QuickJS JavaScript engine ☛ is embedded as a
.wasmmodule namedwasmedge_quickjs.wasmcd ~/OneDrive/WA git clone https://github.com/second-state/wasmedge-quickjs cd wasmedge-quickjs # AOT compilation for better performance: curl -OL https://github.com/second-state/wasmedge-quickjs/releases/download/v0.5.0-alpha/wasmedge_quickjs.wasm wasmedge compile ~/OneDrive/WA/wasmedge-quickjs.wasm wasmedge_quickjs.wasmExample What_year_.js

const d = new Date(Date.now()); console.log(d.getFullYear());Doc.: “
--dirBinding directories into WASI virtual filesystem. Each directory can be specified as--dir`host_path`. You can also map a guest directory to a host directory by--dir`guest_path:host_path`, where `guest_path` specifies the path that will correspond to `host_path` for calls like `fopen` in the guest. The default permission is `readwrite`, however, you can use--dir`guest_path:host_path:readonly` to make the mapping directory become a read only mode.”cd ~/OneDrive/WA/wasmedge-quickjs wasmedge --dir .:. ./wasmedge_quickjs.wasm ./What_year_.jsExample Barcode_checksum.js

// https://bellard.org/quickjs/quickjs.html#Global-objects import * as process from 'process'; // The standard library is included by default in the command line interpreter. // It contains the two modules std and os and a few global objects. // print("Command line is... ", ...args); // 'print' <=> 'console.log' const Thirteen = 13; if (args.length !== 2) exit(-1); if (args[1].constructor.name !== 'String' || args[1].length !== Thirteen) // EAN13 only... exit(-2); const barcode = new Array; args[1].split("").forEach(s => { // Each number within the input string... const element = parseInt(s); // Conversion... if (isNaN(element)) exit(-3); else barcode.push(element); }); // print(...barcode); function Barcode_checksum() { // Méthode : https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/EAN_13#Calcul_de_la_cl%C3%A9_de_contr%C3%B4le_EAN_13 // '471-9-5120-0288-x' with 'x' as check sum (i.e., 'x === 9') // '7', '9', '1', '0', '2', '8': const remainder = (barcode.filter((element, index) => index % 2 !== 0) .reduce((result, element) => result + 3 * element, 0) + // '4', '1', '5', '2', '0', '8': barcode.filter((element, index) => index % 2 === 0 && index !== Thirteen - 1) .reduce((result, element) => result + element, 0)) % 10; return remainder === 0 ? 0 : 10 - remainder; } print(Barcode_checksum() === barcode[Thirteen - 1] ? "CORRECT" : "INCORRECT"); // For test only: for (const k in process.env) print(k, '=', process.env[k]);macOS
cd ~/OneDrive/WA/wasmedge-quickjs wasmedge --dir .:. wasmedge_quickjs.wasm Barcode_checksum.js 3200000003774; echo $?Windows PowerShell
cd ~/OneDrive/WA/wasmedge-quickjs wasmedge --dir .:. wasmedge_quickjs.wasm Barcode_checksum.js 3200000003774; echo $LastExitCodeExercise
Barcode_country.jsconst ISO_3166_international_code = Object.freeze({ Austria: 36, France: 250, Monaco: 492, Portugal: 620, Japan: 392, Russia: 643, Taiwan: 158, Incorrect: -1, Invalid_format: -2 }); const Countries = new Map; Countries.set(ISO_3166_international_code.Austria, [900, 919]); Countries.set(ISO_3166_international_code.France, [300, 379]); Countries.set(ISO_3166_international_code.Monaco, [300, 379]); Countries.set(ISO_3166_international_code.Portugal, [560, 560]); Countries.set(ISO_3166_international_code.Japan, [450, 459]); Countries.set(ISO_3166_international_code.Russia, [460, 469]); Countries.set(ISO_3166_international_code.Taiwan, [471, 471]); const Thirteen = 13; if (args.length !== 2) exit(ISO_3166_international_code.Invalid_format); if (args[1].constructor.name !== 'String' || args[1].length !== Thirteen) // EAN-13 only... exit(ISO_3166_international_code.Invalid_format); // 'Barcode_country' function here...
Barcode_country.jscont'dfunction Barcode_country() { const country_code = parseInt(args[1].substr(0, 3)); if (isNaN(country_code)) return ISO_3166_international_code.Invalid_format; const result = new Array; Countries.forEach((value, key) => { if (country_code >= value[0] && country_code <= value[1]) result.push(key); }); // 'result[0]' raises problem between, for instance, 'France' and 'Monaco': return result.length === 0 ? ISO_3166_international_code.Incorrect : result[0]; }
macOS
cd ~/OneDrive/WA/wasmedge-quickjs # '643' is displayed wasmedge --dir .:. wasmedge_quickjs.wasm Barcode_country.js 4606453849072; echo $?Windows PowerShell
cd ~/OneDrive/WA/wasmedge-quickjs # '643' is displayed wasmedge --dir .:. wasmedge_quickjs.wasm Barcode_country.js 4606453849072; echo $LastExitCodeHost function ☛
Installation of WasmEdge Go SDK
# Unavailable: go install github.com/second-state/WasmEdge-go/wasmedge@v0.14.1 # List of all packages: go list ...
General installation ☛
macOS
brew tap fermyon/tap; brew install fermyon/tap/spinVersion and help
spin -V; spin -hApp. development ☛
macOS
brew install ffmpegWindows PowerShell
choco install ffmpegVersion and help
ffmpeg -version; ffmpeg -help